Understanding Your Hearing Test Chart and Results
After your hearing test, your audiologist will usually review a chart that

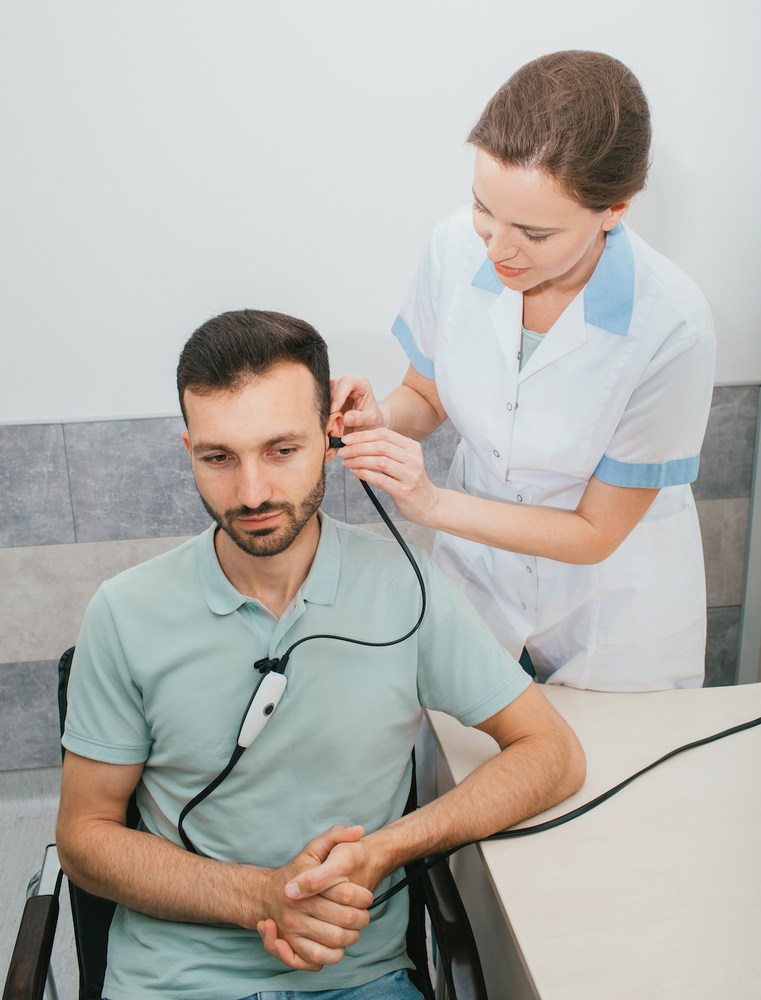
After your hearing test, your audiologist will usually review a chart that

Wearable technology has expanded beyond fitness tracking to include

Hearing care has made impressive progress over the years, from basic